Xsphera Virtual Tumor (XVT) Model
Xsphera Virtual Tumor (XVT) Model
Predictive AI, Built on Human Tissue Response Data
Predictive tumor modeling demands more than baseline molecular profiles. Models must learn how the complex and dynamic tumor microenvironment responds to therapeutic intervention. Capturing these dynamics requires high-quality perturbation data: measured responses of human tumor samples to therapies across doses, combinations, and timepoints.
Xsphera’s Virtual Tumor (XVT) model is trained on thousands of patient samples, each exposed to multiple therapies. By learning response trajectories rather than static states, XVT captures how tumors adapt, compensate, and fail under drug pressure. The model produces patient-specific predictions of treatment efficacy and resistance mechanisms, turning complex biology into actionable clinical and drug development decisions.
The XVT Data Advantage
Why high-resolution human response data is the foundation of predictive oncology AI
A predictive model is only as strong as the data it is trained on. In the clinic, response data is inherently constrained: patients can only be given a single therapy, and outcomes are assessed weeks or months later using coarse, categorical endpoints such as “responsive” or “non-responsive.” While necessary for patient care, these labels offer limited insight into the early biological changes that drive efficacy, resistance, or failure—creating a fundamental bottleneck for training predictive AI.
Xsphera’s ex vivo platform overcomes this limitation by generating rich, high-dimensional response signatures that capture the immediate, proximal effects of therapy on human tumor tissue. This data reveals dynamic gene-level changes that encode mechanism of action and biological state transitions. By designing XVT to predict detailed differential gene expression rather than a binary outcome, the model is trained on information-dense signals that support interpretability, generalization, and continuous improvement as the dataset scales.
XVT Architecture: A Foundation Model for Tumor Response
Deep learning framework to transform initial state to detailed treatment response
We use a custom autoencoder design which encodes both baseline patient RNA profiles as well as treatment and dosage parameters. Our trained predictor network then uses these embeddings to predict the detailed treatment response (RNA differential expression for each gene).
This neural network design has similarities to popular LLMs such as ChatGPT: both learn compact, high-dimensional representations from complex data and use those representations to generate detailed, context-specific outputs. In our case, the model learns a latent representation of tumor state and therapeutic context, enabling it to generalize across patients, treatments, and doses to predict nuanced, gene-level responses. Rather than learning the meaning of words in different contexts, our model learns the relationships between genes and how those relationships and magnitudes shift in response to therapeutic perturbation.
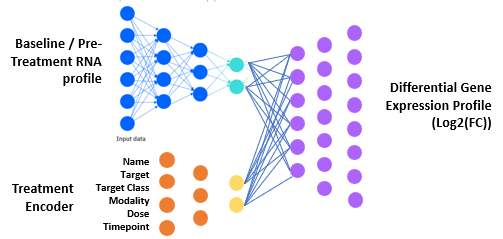
Conceptual model diagram highlighting how baseline RNA profiles are input into the model along with treatment and dosage information. The model then runs these inputs through a multi-level neural network, which is trained to predict differential gene expression response.
Insight from Gene Embeddings
High consistency with known biology + novel functional gene modules
After training XVT, we sought to understand what the model had learned and whether its internal representations were consistent with known biology. We analyzed patient sample embeddings and performed virtual perturbation experiments to assess how predicted responses change with systematic shifts in the input RNA profiles. To further characterize functional relationships, we trained the model to generate gene embeddings and visualized them using a two-dimensional t-SNE projection (shown below).
The resulting gene clusters showed strong alignment with established biology, clearly highlighting canonical pathways such as Type I interferon signaling and MHC class II antigen presentation. In addition, the model identified previously uncharacterized gene groupings that correspond to response patterns observed in our ex vivo experiments. Together, these results indicate that XVT is learning not just static co-expression, but functionally meaningful response relationships shaped by therapeutic perturbation.
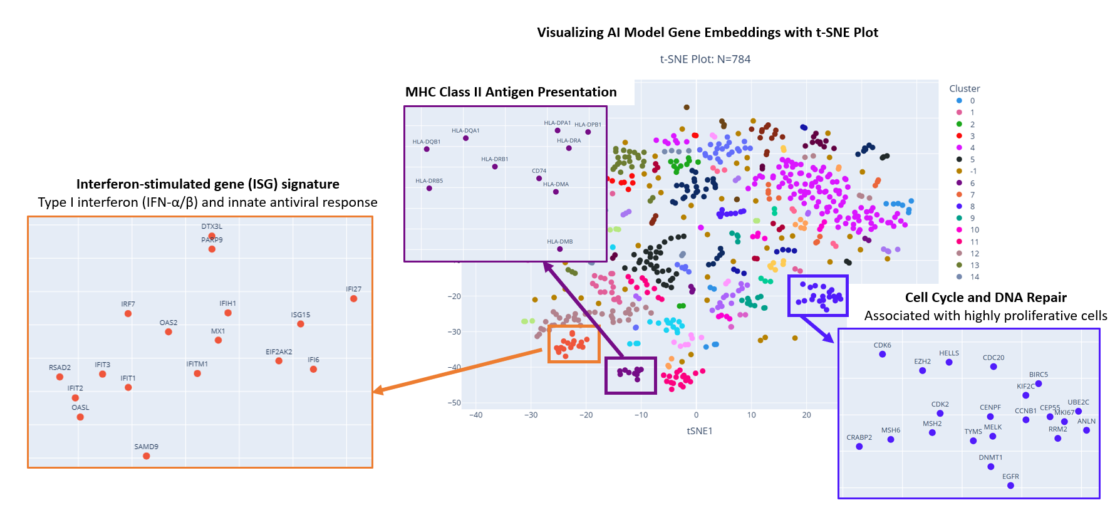
This figure shows a t-SNE plot of the gene embeddings: each dot in the plot corresponds to one gene and genes with similar embeddings are positioned close together. Inspection of the tight clusters confirms several gene groupings are highly consistent with canonical pathways. We also find other clusters that are uniquely grouped according to therapeutic response patterns and changes in cell abundance.
XVT Predictive Accuracy
We’re establishing high standards for model validation
Robust validation is critical to ensure that Xsphera Virtual Tumor (XVT) delivers reliable and actionable predictions. Following best practices, we systematically evaluate model performance using “hold-out” samples that are not used during training.
Active studies are ongoing to assess how predictive accuracy improves as our dataset grows, helping ensure that XVT continues to provide meaningful and biologically grounded insights.
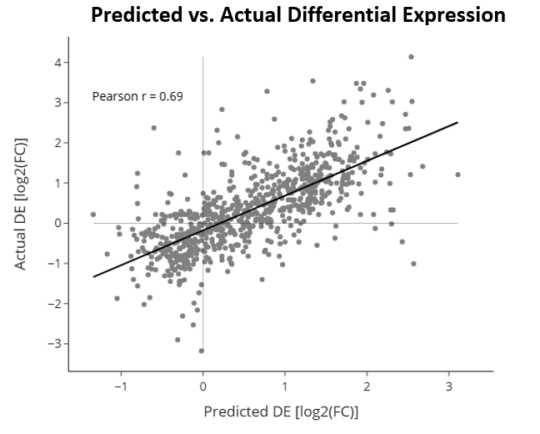
Example of predicted vs. actual gene expression changes for a NSCLC sample treated with an ICI therapy, that was withheld from the model training and development
XVT Modeling Advantages
Shared learning enables scalable, data-efficient predictions
- Base model trained on multiple indications: XVT training data includes 7+ cancer indications
- Temporal modeling: XVT training data includes one or more timepoints for response measurement
- Treatment inputs: Includes modality, target, and dosage, therefore leveraging commonality between treatments =
XVT Use Cases
Scalable insights across therapies, patients, and indications
- Predict treatment response across larger “virtual cohorts” of patients
- Benchmark new therapies against standard-of-care treatments.
- Evaluate combination therapies, including those not previously tested.
- Evaluate responsiveness across cancer indications
- Support clinical patient selection and ex vivo experimental design.
- Counterfactual testing: Supports “what-if” scenarios, revealing patterns and guiding experimental hypotheses.
Fine Tune XVT for Your Pre-clinical Therapy
The XVT model can be trained with additional data from ex vivo testing on your unique pre-clinical therapy. We would begin with designing an experimental study to test your therapy, and decide on the following parameters:
- Cancer indication(s)
- Dosage
- Timepoints
- Any SOC combinations
After sufficient data generation, the XVT model would be re-trained and then available for model inference on different use cases, including evaluating response on larger patient population, evaluating response behavior across other indications, benchmarking vs. SOC treatments, or developing patient selection criteria for clinical trials.
Partner with Us
We are looking for strategic partners to help bring XVT into broader use. Whether in drug discovery, preclinical testing, or clinical research, we aim to collaborate with organizations that want to leverage predictive tumor modeling to accelerate development, generate actionable insights, and explore new therapeutic possibilities.
© 2026 Xsphera Biosciences
26 Landsdowne Street
Cambridge, MA, 02319 — ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
